What is Fetal Alcohol Syndrome?
Fetal Alcohol Syndrome (FAS) is now often referred to as Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders (FASDs) as an inclusive way to discuss the broader range of developmental disorders that can occur as a result of children exposed to alcohol while in utero. Risk factors to keep in mind include a long history of alcohol abuse, poor nutrition, having a previous child with FAS, and genetic susceptibilities. FAS is generally preventable by avoiding the consumption of alcohol during pregnancy. If you have questions about FAS or related concerns, we encourage you to reach out to Oasis Recovery to speak with a specialist who can provide you with more information.
What Causes Fetal Alcohol Syndrome?
In short, Fetal Alcohol Syndrome (FAS) is caused by a woman drinking alcoholic beverages during her pregnancy. Imbibing any type of alcohol has the potential to cause FAS. This includes but is not limited to:
- Hard Liquor
- Cocktails
- Wine
- Beer
- Hard seltzers
- Hard cider
- Hard lemonade
- Hard iced tea
- Homemade liquors
Any alcohol a woman drinks while pregnant enters her bloodstream and passes into the developing fetus through the umbilical cord. Because the baby is not yet developed, the fetus does not have the ability to break down alcohol through the liver or other organs. This results in the fetus being exposed to the same quantity of alcohol present in the mother’s bloodstream and for an extended period of time.
What Is the Effect of Alcohol on a developing Fetus?
Alcohol can interfere with the normal development of the fetus. Alcohol can specifically affect the development of the brain and central nervous system.
Damage alcohol may cause a fetus can include:
- Brain damage
- Abnormal physical development
- Altered neurotransmitters and their functions
- Oxygen deprivation to the fetus resulting in lack of nutrients
Symptoms of Fetal Alcohol Syndrome
The symptoms of Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders (FASDs) can include:
- Atypical physical features
- Smaller head
- Shorter height
- Low body weight
- Poor coordination
- Vision problems
- Hearing problems
- Memory issues
- Lower aptitude
- Delayed speech and language development
- Poor judgment when it comes to decision-making
- Difficulty concentrating
- Hyperactivity
Fetal Alcohol Syndrome is correlated with heart, kidney, and muscular structural issues.
There are neurological issues that are common for children who has been exposed to alcohol while in fetal development. Individuals with FAS may have difficulty establishing appropriate social boundaries throughout childhood. They may seek excessive physical contact and be hyperactive, or they might have memory problems, have a short attention span, and have difficulties with their motor skills. These issues can include a wide range of intellectual disabilities including:
- Learning problems.
- Poor performance in school
- Poor memory
- Short attention span.
- Poor judgment
- Impulsivity
Fetal Alcohol Syndrome in Adults
FAS can cause a number of physical complications that persist into adulthood. However, these problems may appear less severe in adults than in children. These include:
Physical Signs
- Small head
- Short height
- Thin upper lip
- Small brain size
Mental/Behavioral Signs
- Poor memory
- Lack of concentration
- Aggression
- Lack of decision-making skills
- Anxiety
- Depression
- Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder
How to Prevent Fetal Alcohol Syndrome
As stated previously, a pregnant woman who drinks alcohol can cause fetal alcohol syndrome in her child. When a woman drinks while pregnant, her blood flows through her body, through the placenta, and to the developing fetus. Because a fetus breaks down alcohol at a much slower rate than an adult, it takes longer for the alcohol to leave their bodies, leading to fetal alcohol syndrome. Even small amounts of alcohol have been shown to cause fetal alcohol syndrome, if a woman consumes a lot of alcohol while pregnant. You must abstain from alcohol if you’re pregnant to avoid fetal alcohol syndrome.
How to Treat FAS
The effects of FAS do not go away. Keeping that in mind, it’s possible that early intervention (particularly before the age of 6) treatments can improve a child’s development and help them normalize and integrate into school.
There are mediations that can treat and alleviate some of the symptoms associated with FAS.
Other treatments can include:
- Behavior therapy
- Education therapy
- Parental training
A stable home environment and a loving, supportive family can make a huge difference in the life of a child. Preventing a child from experiencing acts of violence of exposure to extremely negative experiences that cause fight or flight responses is important in early childhood development. Making use of special education and social services can also help a child with developmental delays catch up to their peers and better fit in.
Signs of Alcoholism
When someone is addicted to alcohol, they experience difficulty controlling their alcohol use, become focused on alcohol, or continue consuming alcohol despite it causing problems. Withdrawal symptoms are also a feature of this condition, where you require more alcohol or abruptly stop drinking to achieve the same effect.
Approximately 5% of women suffering from an alcohol use disorder birth children who are eventually diagnosed with Fetal Alcohol Syndrome. The following are indicators that an individual may be suffering from alcoholism:
- Unable to cease drinking or control the amount consumed
- Self-isolation
- Continuing to consume alcohol despite negative consequences
- Neglecting family, work, or social commitments
- Developing an increasing tolerance to alcohol and its effects
- Experiencing withdrawal symptoms if alcohol is not consumed
- Legal problems
- Financial problems
- Slurred speech
- Change in appearance such as weight gain/loss
- Disheveled appearance
Scope of Alcoholism within the United States
Today, more than 86 percent of U.S. adults over the age of 18 say they have consumed alcohol at some point. 70 percent of those surveyed said they consumed alcohol in the last year, and 56 percent consumed alcohol in the last month. Despite this, American’s relationship with alcohol is far from being considered healthy. Below is a graph displaying the real problem Americans have with alcoholism:
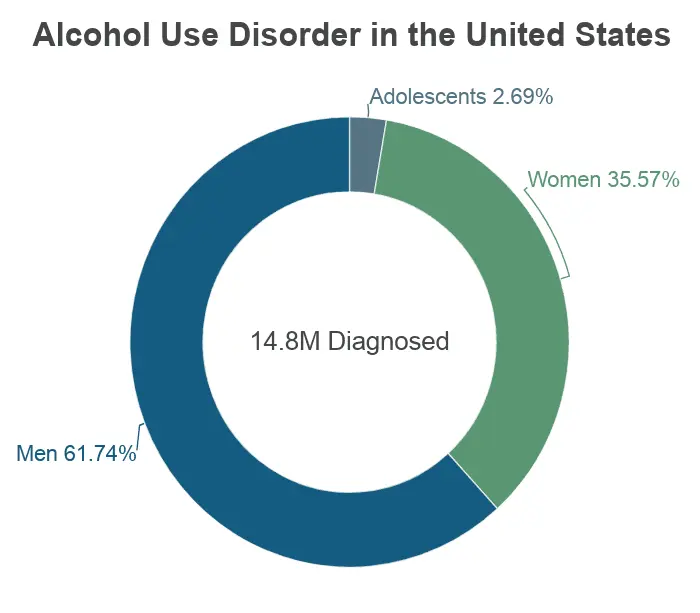
Despite the fact that America has one of the lowest alcohol consumption rates among first-world nations, we have one of the highest rates of alcohol addiction. Around 15 million American adults suffer from an alcohol use disorder. The following graph illustrates the prevalence of alcoholism in the US in comparison to the world:
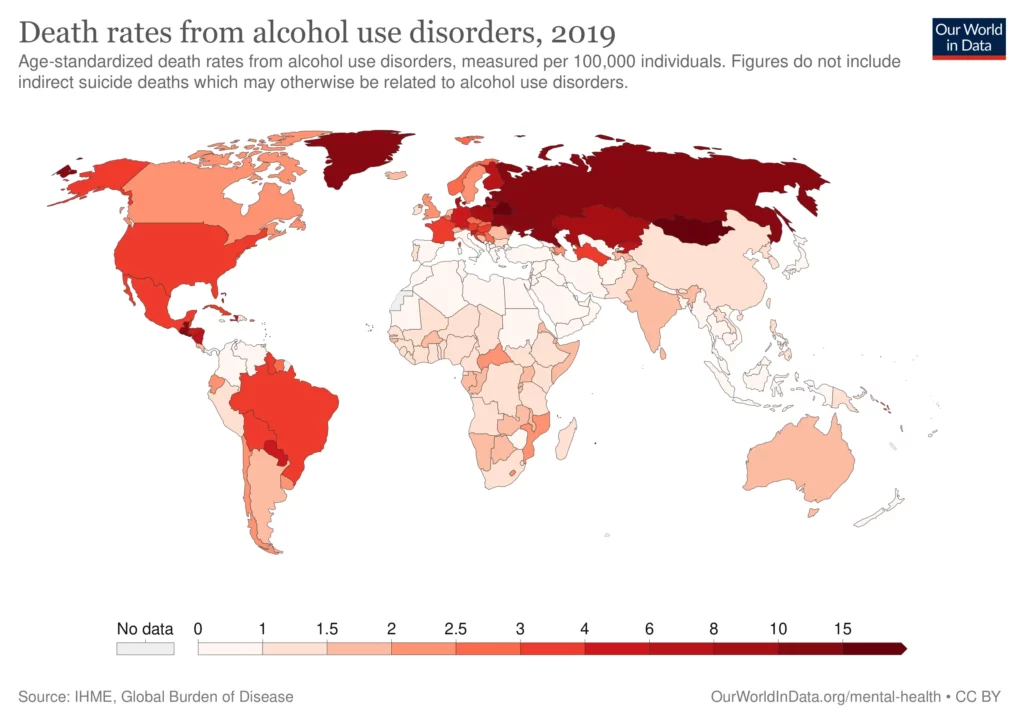
Although the United States isn’t a leading nation in terms of alcohol consumption, it is leading in the disease of alcoholism. Fetal Alcohol Syndrome is one of many negative consequences of abusing alcohol. There are many adverse reactions that come from alcoholism if left untreated.
Dangers of Untreated Alcoholism
Untreated alcohol abuse can have serious, lifelong, and potentially fatal effects on the consumer. This substance’s effects are not isolated to one part of the body. Alcohol slowly poisons the whole person. The following are the various side effects of untreated alcoholism:
- Liver damage – Your liver is responsible for eliminating alcohol from your body, but it may not be able to keep up if you consume too much at once. Liver cells may be killed by alcohol, leading to scarring known as cirrhosis. Long-term heavy consumption of alcohol can also lead to alcoholic fatty liver disease, a sign that your liver is not functioning as well as it should.
- Heart Disease – Blood clots, fat and cholesterol levels are no laughing matter. Alcohol makes both of them worse. Heavy drinkers have been shown to have a higher mortality rate due to heart disease because they have trouble pumping blood to their heart.
- Cancer – Heavy alcohol consumption is connected to many kinds of cancer. Your mouth, throat, voice box, and esophagus are all damaged by alcohol. Your liver, breasts, and intestines can be afflicted with cancer due to the presence of alcohol. Alcohol makes it easier for cancer-promoting chemicals in tobacco and other sources to gain access to your cells.
- Brain damage – Alcohol impacts the brain’s communication networks, making it more difficult for you to think and speak clearly, remember things, make decisions, and move. Furthermore, mental health issues such as dementia and depression can be caused by excessive drinking. You may suffer long-term nerve damage even after you sober up, which may result in pain.
Contact Oasis Recovery to Stop Alcohol Abuse Today
If you or someone you care about has an alcohol abuse disorder (AUD) and is pregnant or plans to become pregnant, Oasis Recovery can help them break the cycle of abuse. Drinking while pregnant can result in Fetal Alcohol Syndrome. Many of the outcomes associated with FAS are irreversible. Call us today to speak with a recovery specialist about the risks associated with FAS and alcohol addiction.