Is Alcohol or Codeine More Dangerous to Drink?
Do you know much about codeine? Perhaps you tried it because one of your friends told you it was an easy way to get high. You may have even heard that drinking alcohol with it made it even more fun. It is time that you knew the truth.
Have you accidentally become addicted to codeine? Now, before you pick up that bottle of liquor to try to swap one habit to get rid of the other, we at Oasis Recovery ask that you please take a moment to read this quick article.
Why Codeine is Dangerous
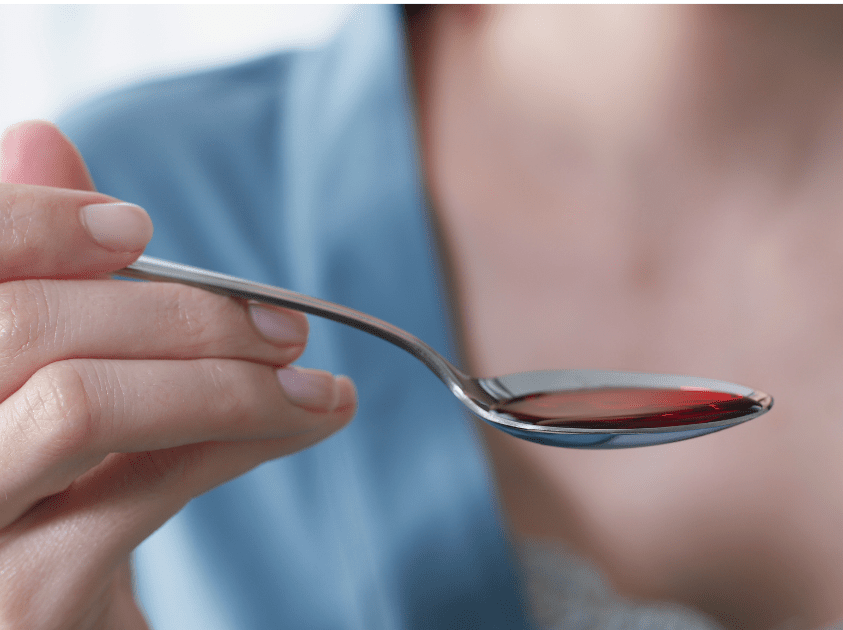
Codeine is particularly dangerous because it is sold in the form of cough medicine, making it easy to get your hands on. It is an opioid pain medication, which places it into the classification as a narcotic drug. Although it is less potent, it produces similar effects as morphine, when taken in high enough doses.
It is a commonly-held belief that codeine is relatively harmless. This misconception may cause people to become addicted, or to try other opiate drugs when they are no longer getting high from the codeine. What makes codeine exceptionally dangerous is that if you drink enough of it, your breathing can slow down so much that you might stop breathing altogether.
Some people try and drink alcohol with codeine, thinking that they can make themselves feel even better. Codeine and alcohol are a deadly mix. If you try and drive or operate machinery while on codeine, you risk your life. Your reaction time is slowed and you may become dizzy or severely drowsy.
It is also possible to have an allergic reaction to codeine. Seek emergency care if you break out in hives, can’t breathe, or have swelling of your face, lips, tongue, or throat. There are other medications that when mixed with codeine can cause dangerous side effects or death. Here are a few examples:
- Cold or allergy medicines, or diuretics
- Sedatives akin to Valium
- Sleeping pills, muscle relaxers or mental illness medications
- Depression medications, medicines for migraines
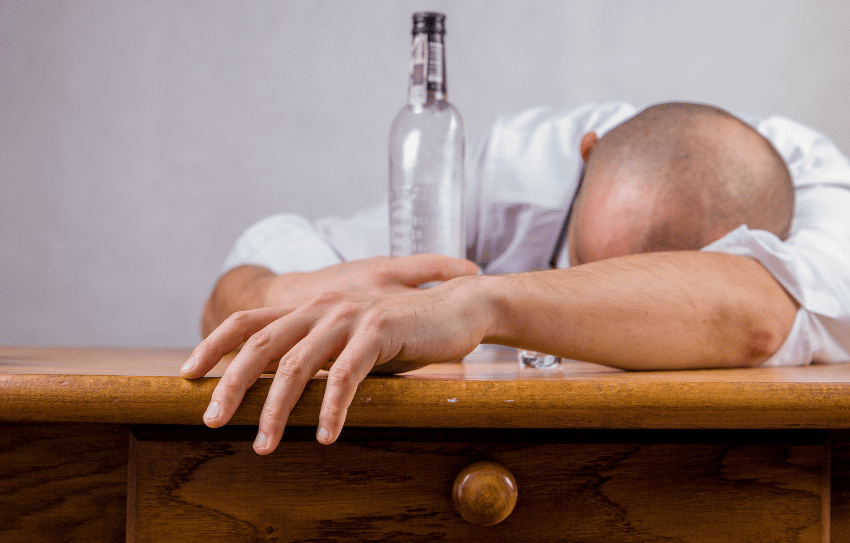
The Dangers of Drinking Alcohol Excessively
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, from 2011-2015, excessive alcohol use led to about 95,000 deaths each year in the United States. It is clear that the short and long-term health risks of an alcohol addiction make it a dangerous pastime.
Here are some short-term consequences that can be blamed on excessive drinking:
- Alcohol poisoning
- Violence: which includes homicide, suicide, domestic violence and sexual assault
- Stillbirth, miscarriage and fetal alcohol disorders
- Risky sexual behaviors that may result in STDs or unintended pregnancies
The long-term health risks of drinking alcohol excessively are just as bleak:
- Alcohol addiction
- Social and family problems, often unemployment
- Learning and memory problems which may include dementia
- Weakened immune system
- Higher risk of cancer
- High blood pressure, heart disease, liver disease and stroke
Is One More Dangerous Than the Other?
When examining the side effects of alcohol versus codeine, one thing is clear. In both cases, moderation is key.
Codeine may be used safely by many people when prescribed by a doctor for pain relief. However, when it is abused for the purpose of “feeling good,” this opiate takes on a whole new dangerous dimension. Your desire to have more codeine takes the form of an addiction and you risk an overdose.
The same is for alcohol. If you can safely enjoy one glass of wine and stop right there, you aren’t drinking excessively, unless you are an alcoholic. However, alcohol becomes very dangerous when you aren’t able to control your impulse to consume it.
Therefore, the answer must be that they are equally dangerous. Abusing either codeine or alcohol is nothing but a dead-end street.
Eliminate Your Addiction With Oasis Recovery
Whether you are struggling with codeine addiction, an alcohol addiction, or both, we at Oasis Recovery are here to encourage you, and see you through until you are clean again. Have faith that with our help, you can accomplish what you set out to do. Reach out to an addiction specialist today.